GGSIPU Data Structures Question Paper (Dec 2025) | B.Tech AIDSA/AML/10T-201
Are you preparing for the GGSIPU B.Tech 3rd Semester finals? Understanding the exact nature of university questions is the first step toward a high score. For students in the AI & DS and AI & ML branches, the Data Structures (AIDSA/AML/10T-201) paper is often the most challenging part of the curriculum.
In this post, we are sharing the complete End Term Examination paper from Dec 2025-Jan 2026. By reviewing this official GGSIPU Previous Year Paper, you can get a clear idea of how the 60-mark weightage is distributed across Unit-I to Unit-IV. This paper includes critical questions on Binary Search Trees (BST), Quick Sort partitions, and Dijkstra’s Algorithm, giving you a direct look at the difficulty level expected by the University.
Use this as a reference to test your speed and accuracy before the real exam day.
| END TERM EXAMINATION | |
| Third Semester [B.Tech] | Dec 2025-Jan 2026 |
| Paper Code: AIDSA/AML/10T-201 | Subject : Data Structures |
| Time:3 Hours | Maximum Marks:60 |
| Note: Attempt all questions as directed. Internal choice is indicated. | |
| Q1 Answer the following in brief. (Any four) (4×5=20) | |
| (a) Write an algorithm for Depth First Search (DFS). Give an example. | |
| (b) Convert the infix expression (A + B) * (C − D / E) / H to postfix notation.. | |
| (c) Show all the steps and final output of Heap sort on array X = [29, 13, 14, 6, 7, 8]. | |
| (d) Write an algorithm to insert a node in a singly linked list. | |
| (e) A hash table of size 10 stores 6 elements. If linear probing is used, what is the load factor (α)? What happens if α > 1? | |
| (f) Differentiate between Eulerian and Hamiltonian paths with example. | |
| (g) Construct a Binary Tree using the following In-order and Pre-order traversals of a tree:
INORDER : D G B A H E I C F |
|
| (h) What is a Complete binary tree? If the number of nodes in a complete tree is 100000, find its depth. | |
| Q2. a) A circular queue of size 5 initially empty is given. If the following operations are performed:
Insert(11), Insert(23), Insert(34), Delete(), Insert(45), Insert(50), Insert(60). |
|
| Q2. b) What is Algorithmic Complexity and explain its importance? (3) | |
| OR | |
| Q3. a) Implement a Queue using arrays and demonstrate enqueue and dequeue operations with the help of an example. What are its various applications? (6) | |
| Q3.b) Give the features of various data structures such as List, Set, Tuple and Dictionary. Give an example of each. (4) | |
| Q.4 a) Sort the array A = [29, 10, 14, 37, 13] using Quick Sort with last element as pivot. Write the sequence of swaps and the final sorted output. (5) | |
| Q4. b) What do you mean by time and space trade-off? Define various asymptotic notations and derive the Big O notation for linear search. (5) | |
| OR |
|
| Q5.a) Perform Merge Sort on array A = [13, 12, 14, 6, 7, 8]. Show how the array is divided and merged in a step-by-step manner. (5) | |
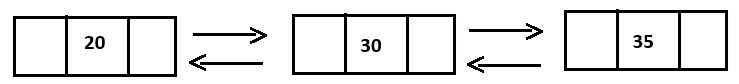
| Q5. b) Consider a circular doubly linked list as below:
|
|
| Perform the following operations and show the procedure: | |
| 1. Insert the node 10 at the beginning. 2. Delete node at the end (5) | |
| Q.6 a) Construct a Binary Search Tree (BST) by inserting the following sequence of keys in order: 45, 12, 77, 34, 55, 94, 25, 50. Then, delete 55 and show the updated tree. (7) |
|
| Q6. b) Explain how tree balancing affects search performance. (3) | |
| OR | |
| Q.7 a) Explain tree in order traversal. Draw an example with 5 nodes. (5) | |
| Q.7 b) An AVL Tree has the sequence [60, 70, 80, 90, 100]. Show rotations after each insertion. (5) | |
| Q8. a) a) For graph: V = {A, B, C, D, E}, Edges = {A→B=2, A→C=3, B→D=5, C→D=1, D→E=2}. Find the shortest path from A to E using Dijkstra’s Algorithm. (6) | |
| Q.8 b) Explain how indexing improves file access time. What is the difference between dense and sparse indices? (4) | |
| OR | |
| Q.9 a) A file contains 1000 records, each record takes 100 bytes, and the block size is 1 KB. Compute: | |
| 1. Block factor (bfr) | |
| 2. Number of blocks required (4) | |
| Q.9 b) Using hash function h(k) = k mod 7, insert keys {10, 20, 15, 33, 47, 28}. Resolve collisions using Linear probing and show the final hash table. (6) | |
Also, check out the other subjects’ Previous Year Papers here.